2022-09
29Why do some flow meters perform poorly in low flow range accuracy?
If the accuracy of both flow meters is 1.0%, then the accuracy of the two instrument products is the same?
Not really! So what's the difference?
We often see letters like RD, F.S., S.P. after precision data, and that's the difference.

Three types of precision products
What do these letters mean? (Taking 1.0% accuracy as an example)
RD (abbreviation for Reading): refers to the reading accuracy, which is ± 1.0% of the actual reading of the flowmeter;
Reading accuracy=(measured data - measured standard value)/measured standard value * 100%
F. S. (abbreviation for Full scale): refers to the full scale accuracy, which is ± 1.0% of the full scale accuracy;
Full scale accuracy=(measured data - measured standard value)/full scale value * 100%
S. P. (abbreviation for Set point): Refers to the precision of the set value, which means that the controller product user can independently set the flow rate within ± 1.0%.
Set value accuracy=(measurement data - set value)/set value * 100%
Actually, S.P. is the same as RD, except that S.P. is used to express controller accuracy and RD is used to express flow meter accuracy.
Let's take a 100L flowmeter as an example and calculate using the above formula at different flow rates to see how the results are:
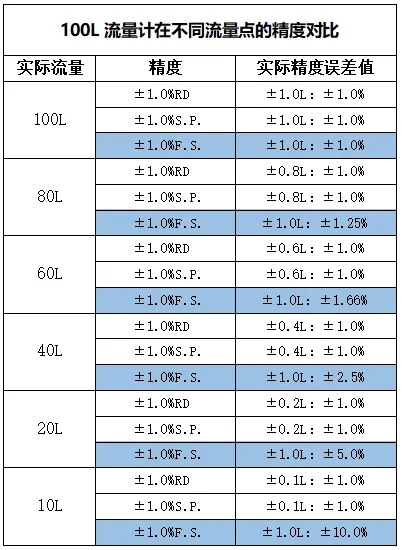
According to the data in the table, when measuring a flow rate of 10L with a 100L flowmeter, the flow error value with ± 1.0% RD accuracy is ± 0.1L, and the flow error value with ± 1.0% FS accuracy is ± 1L, with a precision error difference of 10 times.
So, when choosing a flow meter, attention should be paid to whether the product accuracy data is reading error or full-scale error, in order to choose the product with more suitable accuracy.



